Fast food is all about quick and convenient meals. It’s made fast, using pre-cooked or preheated ingredients, and often comes in packages ready for takeout.
Fast food has been around for centuries, serving as a lifeline for people needing affordable and ready-to-eat meals. From ancient street vendors to modern-day restaurants, the concept of fast food has evolved but its essence remains the same.
What was once a luxury—eating out—has become a daily necessity. In our busy culture, we often don’t have time to cook or sit down for a meal. Fast food meals are popular in the United States. It’s easy to drive through a fast food restaurant and get an inexpensive meal for the family within minutes. This convenience is much more appealing than coming home after an eight-hour work shift, preparing and cooking a meal. Additionally, supermarket prices can be high, and grocery shopping can be time-consuming.
Now, let’s dive into some eye-opening statistics about the fast food industry and how often people are grabbing these quick bites.
What Percentage of Adults Consumed Fast Food on Any Given Day?

Fast food is a staple in the American diet and is linked to high-calorie intake and poor nutrition. Factors like time, money, cost, and accessibility play a significant role in how often people choose to eat fast food.
- It’s well-known that Americans eat a LOT of fast food. According to the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 36.6% of adults consumed fast food on any given day between 2013 and 2016. This means that, on any given day, one out of three Americans will choose to eat at a fast food restaurant. (1)
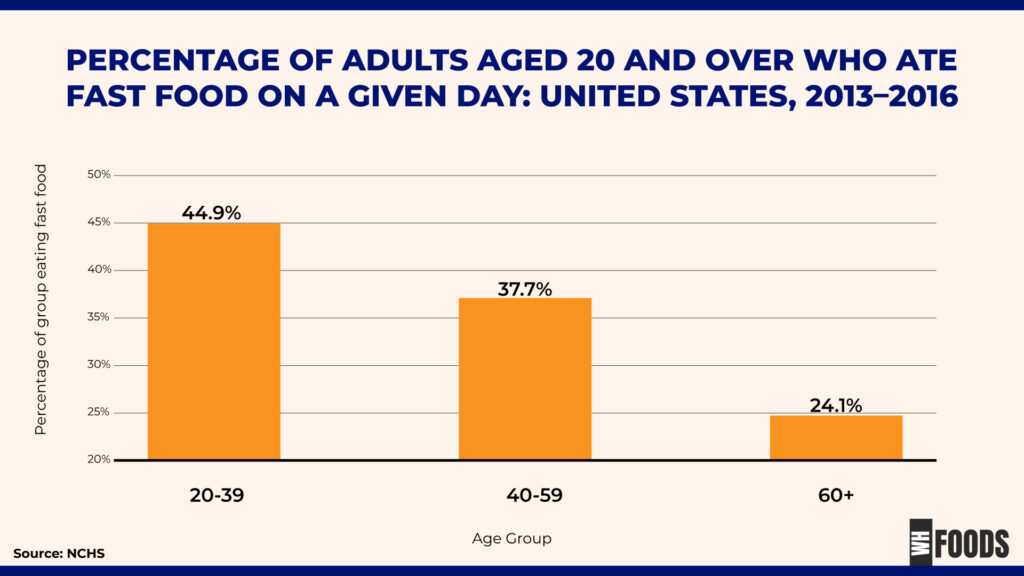
By Age
The percentage of adults who ate fast food decreased with age: 44.9% of younger adults aged 20–39, 37.7% of those aged 40–59, and 24.1% of adults aged 60 and over. Although younger generations emphasize healthy eating, many children and adolescents still get a large portion of their daily calories from fast food. (1)
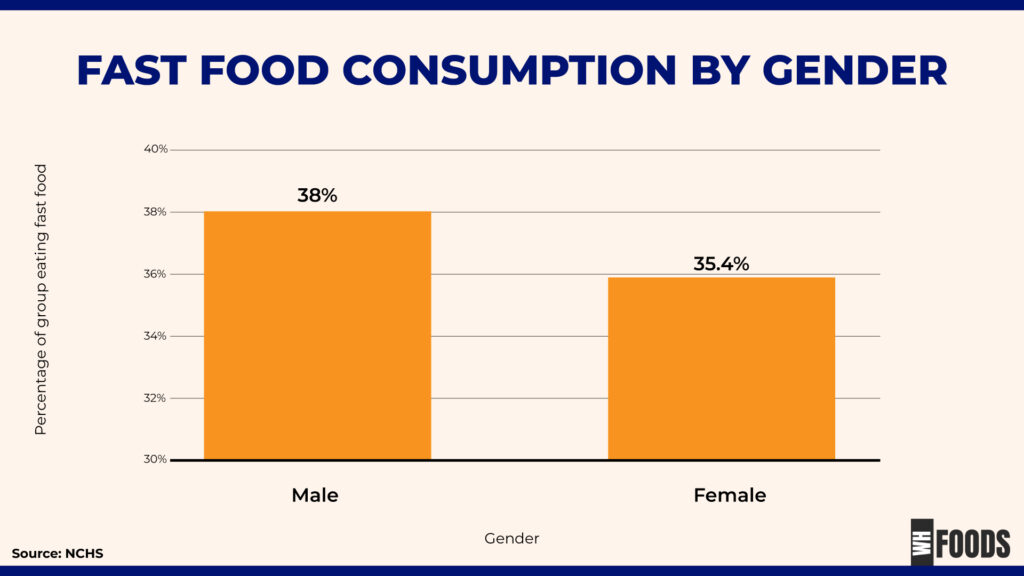
By Gender
Among all adults, a higher percentage of men (37.9%) than women (35.4%) ate fast food. One possible reason is the difference in dietary preferences and habits between genders. Men may tend to choose fast food more often due to factors like taste preferences, nutritional needs, or cultural and societal norms. (1)
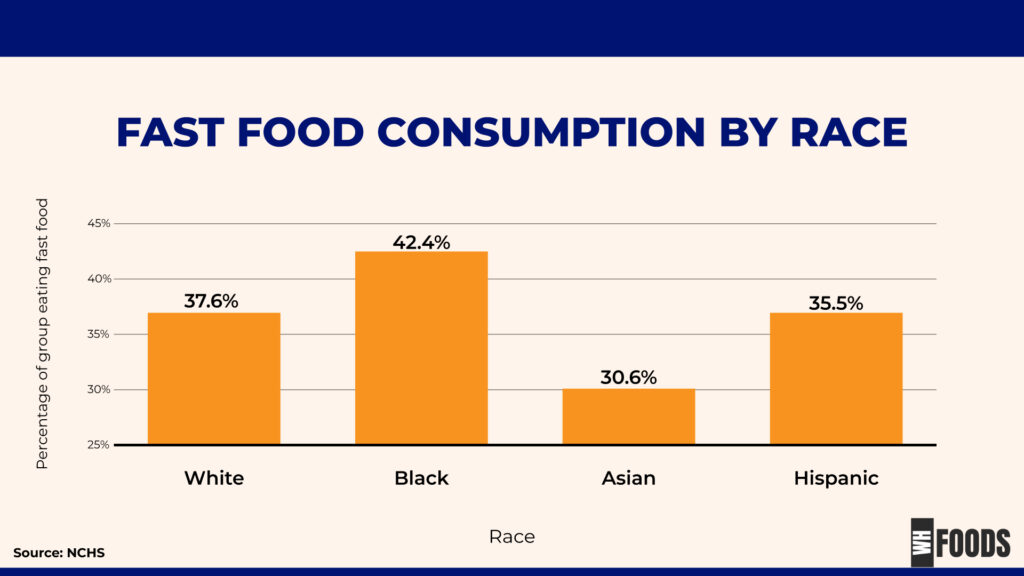
By Race
According to the same CDC report, non-Hispanic Black adults were more likely to consume fast food than non-Hispanic White adults between 2013 and 2016:- Non-Hispanic Black adults: 42.4%- Non-Hispanic White adults: 37.6%- Non-Hispanic Asian adults: 30.6%- Hispanic adults: 35.5% (1)
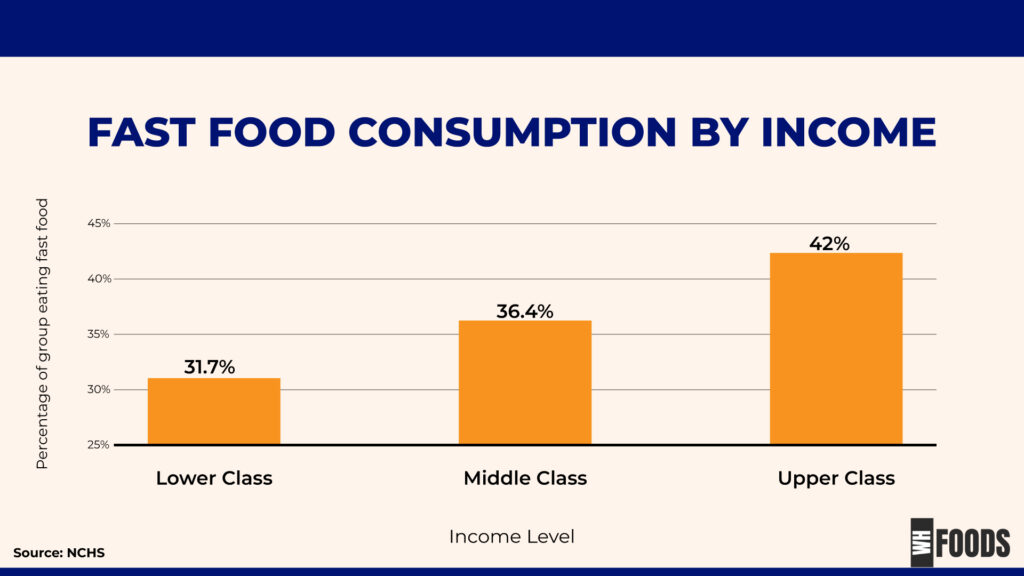
By Income
On a given day, 31.7% of low-income, 36.4% of middle-income, and 42.0% of high-income adults consumed fast food. America is a country full of hard-working people, so time and money are often highly valued. (1)
By Meal
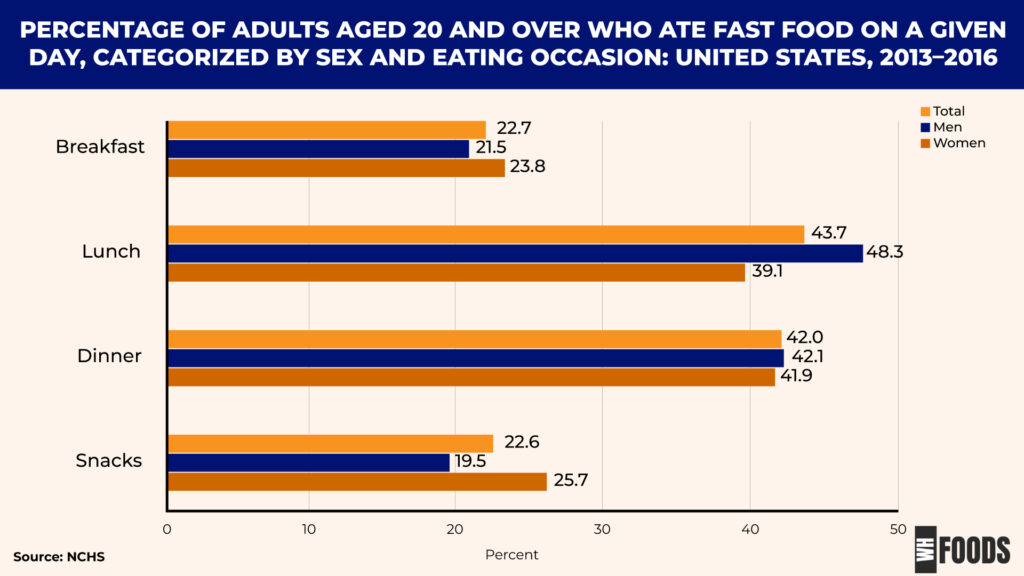
- Among adults who consumed fast food, the most common times were lunch (43.7%) and dinner (42.0%), followed by breakfast (22.7%) and snacks (22.6%). The nearly equal percentages for lunch and dinner suggest that fast food is a convenient choice for those who need a quick meal during work breaks or after a long day. (1)
- A higher percentage of men (48.3%) than women (39.1%) consumed fast food during lunch. Conversely, more women (25.7%) than men (19.5%) ate fast food as snacks. This difference suggests that men may prioritize convenience and speed during their midday meal, possibly due to work commitments or a preference for quick lunches. On the other hand, women may be more likely to turn to fast food for snacks, which could reflect different eating patterns or lifestyle choices. (1)
What Is the Percentage of Children and Adolescents Who Eat Fast Food on Any Given Day?
Despite warnings about obesity and unhealthy diets, American kids and adolescents are eating even more fast food. Consuming too much fast food is harmful to children’s health due to its high-calorie content and lack of essential nutrients. A poor diet can lead to heart problems and obesity.

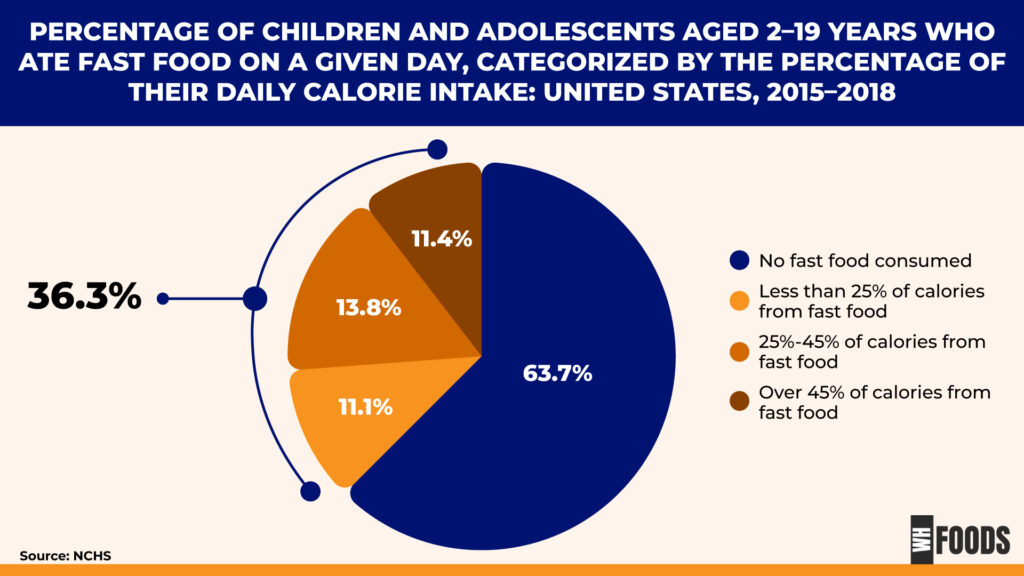
- Between 2015 and 2018, over one-third (36.3%) of children and adolescents ate fast foods on any given day. These findings aren’t surprising given how families today often struggle with limited time and money. Many fast-food meals have become an easy option for stressed families because they are quick, affordable, and convenient. (2)
- Among children and adolescents, 11.1% got less than 25% of their daily calories from fast food, while 13.8% received 25% to 45% of their daily calories from fast food. Adolescents aged 12–19 consumed a higher percentage of their calories from fast food compared to children aged 2–11. (2)
How Much Did Americans Spend on Fast Food?
With inflation driving up prices for everything from gasoline to groceries, many Americans are seeking cheaper dining options. Between January 2021 and January 2023, grocery prices surged, leading consumers to explore more affordable ways to feed their families. Although inflation has slowed, the financial impact continues to push people toward economical choices, including fast food, as a way to manage their budgets.
- The United States leads the world in fast food consumption, with the average American spending an estimated $1,200 annually, contributing to a total of around $110 billion each year. (3)
- The U.S. quick-service restaurant (QSR) sector has grown consistently since 2004, peaking at over $349 billion in consumer spending in 2023. A quick service restaurant, also known as a limited-service restaurant (LSR), is a type of dining establishment that offers meals at a lower price point with fast service, a limited menu, and minimal table service. Outside the industry, these establishments are more commonly referred to as fast-food restaurants. (4)
What Makes Fast Food So Popular in America?

Fast food restaurants are popular mainly because they offer quick and convenient meals at affordable prices. Their wide variety of options and easy accessibility on nearly every street corner make them a go-to choice for many. Additionally, the industry has adapted by providing healthier menu choices to meet changing customer preferences. Rapid urbanization, lifestyle changes, and increased spending by the middle class have also played a role in their popularity.
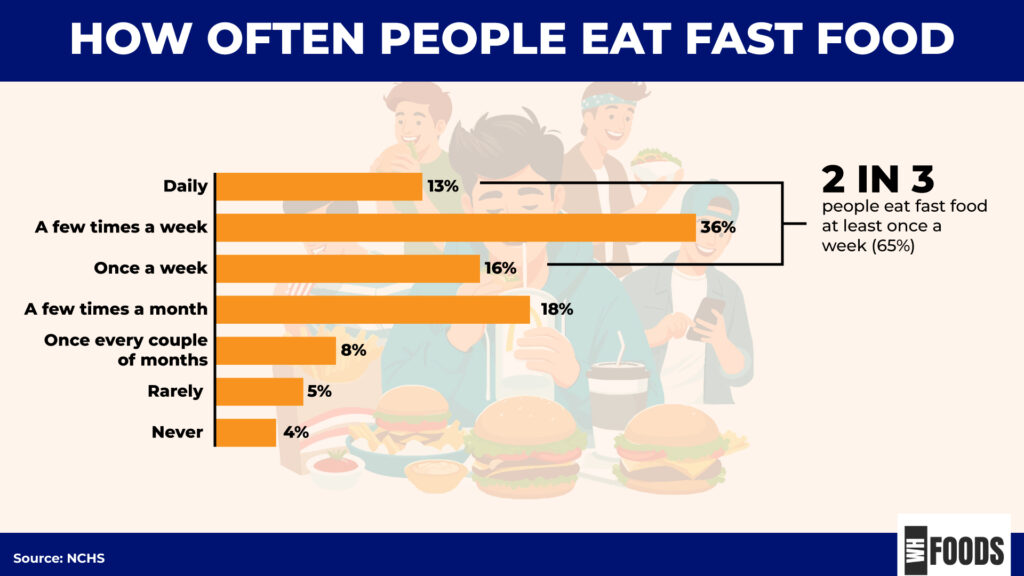
- Approximately 65% of people eat fast food at least once a week. Fast food isn’t just quick, which is essential for busy families—it also eliminates the need to shop, cook, and clean, making it a convenient choice. (5)
- 40% of American consumers use drive-thrus to buy fast food. In a world where drive-thrus can be quicker than grocery store checkouts, it’s no wonder fast food plays a big role in both our diets and the economy. (5)
- Only 4% of people reported not eating fast food at all in the past year. Fast food serves as a unifying factor across diverse lifestyles, from bustling city life to relaxed weekend treats. It appeals to people of all ages, income levels, and educational backgrounds, making it a common thread in our everyday lives. (5).
What Are the Health Risks Associated With Eating Fast Food?
Some people criticize the fast food industry for its impact on society. They argue that eating fast food regularly is unhealthy and that the industry mistreats animals, exploits workers, and harms local cultures by changing people’s tastes away from traditional foods. Additionally, fast food habits are linked to rising rates of overweight and obesity.
- Fast food is a popular meal choice, but it’s often high in calories and low in nutrients. Consuming it frequently can negatively impact almost every part of your body. Eating fast food frequently can harm various parts of your body, potentially raising your risk of developing conditions like type 2 diabetes, obesity, and high blood pressure. (6)

The Most Popular Fast Food Chains
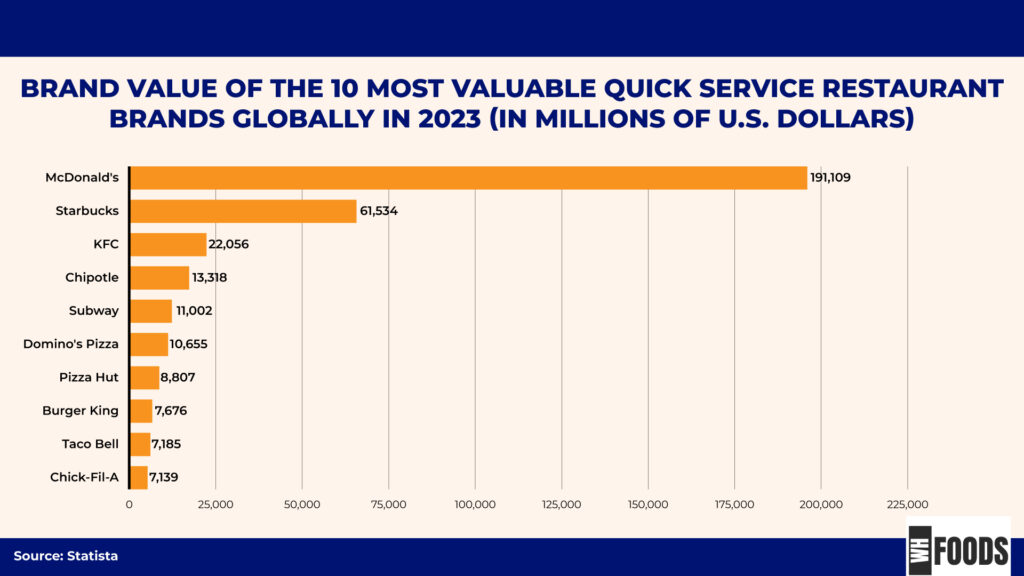
In 2023, McDonald’s was the most valuable fast food brand globally, with an estimated brand value of around 191 billion U.S. dollars. Since the McDonald brothers introduced the fast food concept in 1940, their golden arches have become a symbol of quick, affordable, and tasty meals. Over the decades, McDonald’s has continued to attract customers with its iconic offerings, cementing its place in global food culture. (7)

- That same year, Starbucks followed with a brand value of approximately 61.5 billion U.S. dollars. Looking ahead, Starbucks plans for 90% of its new stores to include drive-thrus, emphasizing convenience and speed. The rise of digital sales and contactless transactions is making fast food even quicker and easier. For instance, Starbucks’ mobile order service has seen a 400% growth over the past five years. (7)
Market Size and Growth in the Online Food Delivery Industry
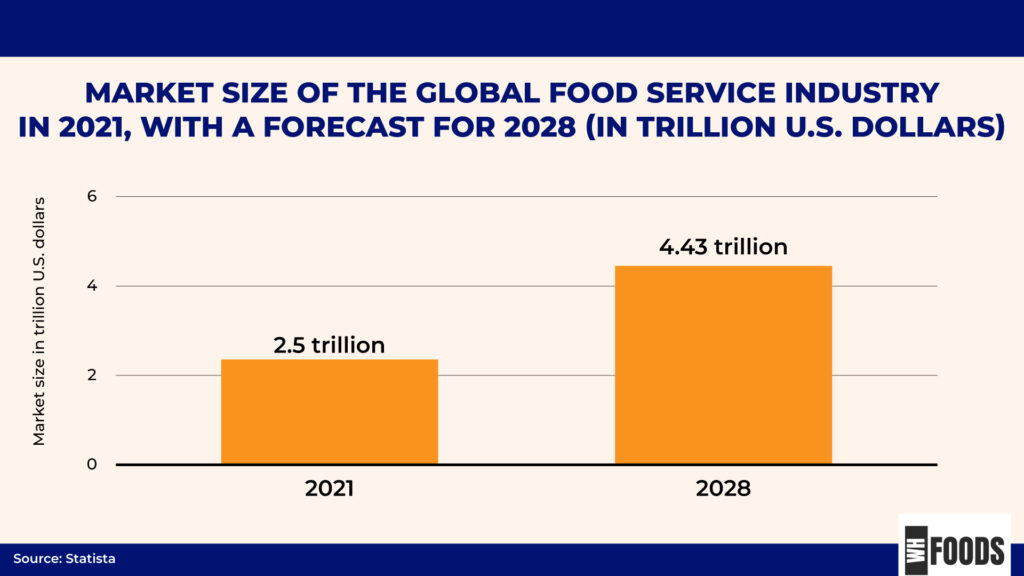
- The market size of the global food service industry was $2.52 trillion in 2021, with a forecast of $4.43 trillion for 2028. While the coronavirus pandemic led to a revenue decline in many food and drink service sectors, figures are now returning to pre-pandemic levels. Forecasts predict future growth, including in the overall industry, as businesses adapt and recover. (8)
- The revenue in the U.S. Online Food Delivery market is expected to reach $353.30 billion in 2024. With an anticipated annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.76% from 2024 to 2029, the market is projected to expand to $562.70 billion by 2029. This growth reflects the increasing demand for online food delivery services as they become more integrated into consumers’ daily lives. (9)
- The global Quick Service Restaurants (QSR) industry continues to expand, with the market size projected to reach $1.1 trillion in 2024, marking a robust growth of 3.6% compared to the previous year. This growth builds on a steady compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3% observed from 2019 to 2024. In 2023, the industry was valued at approximately $1.032 trillion, underscoring the ongoing demand and resilience of the fast food sector. (16)
Facts About Fast Food Industry In the US

In 2023, the market size for the QSR industry reached $387.5 billion. The market size of the Fast Food Restaurants industry in the U.S. has grown at an average rate of 3.4% per year between 2018 and 2023. (10)
- The number of QSR franchise establishments in the U.S. fluctuated from 2007 to 2023, reaching 195,507 in 2023. (11)
- In 2023, 3,676,580 people worked in the fast food industry. They perform various duties, including taking orders, serving food and beverages, and processing payments. They may serve customers directly at the counter or from a steam table and can also be involved in food and beverage preparation. In some cases, counter attendants may also handle waiting tables, providing full service to customers. (12)
- Plant-based foods saw a 6.6% sales growth in 2022, up from 5.9% in 2021, with only a 10% increase in average retail price, resulting in the market value reaching $8 billion. Despite challenges like inflation, lack of scale, subsidies, and shrinking retail space, consumers are clearly showing a growing demand for plant-based foods. This trend indicates a shift in dietary preferences, with more people seeking out healthier and sustainable options in a fast food meal, even in the face of economic pressures. (13)
- During the COVID-19 pandemic, 88.5% of respondents indicated that pickup or drive-thru was their most common method of acquiring fast food. In comparison, 8% of respondents reported that their most common way of dining at fast food restaurants was using alternative seating areas. (14)
- Chipotle’s digital sales surged by 216% year-over-year during the second quarter as the pandemic intensified. Digital sales made up $829 million, or 61%, of all Chipotle’s sales, despite most of its dining rooms being open for sit-down service. (15)
Final Thought
Fast food remains a significant part of American life, with children and families frequently opting for fast food meals from popular fast food establishments like Taco Bell and Pizza Hut. Regular fast food consumption, especially among children, raises concerns reflected in health statistics.
The National Center for Disease Control reports links between high caloric intake from items like french fries and insulin resistance, with a significant difference observed based on family income. As the consumption of fast food remains prevalent, understanding these health impacts is crucial for making informed choices in our fast-paced world.
As the fast food sector continues to grow, it’s crucial to consider these statistics and the impact of fast food brands on our well-being, particularly for the younger generation.
Sources
- NCHS Data Brief: Fast Food Consumption Among Adults in the United States, 2013–2016
- NCHS Data Brief: Fast Food Intake Among Children and Adolescents in the United States, 2015–2018
- World Population Review: Fast Food Consumption by Country 2024
- Statista: Consumer spending in the quick service restaurant (QSR) sector in the United States from 2004 to 2023
- Drive Research: Fast Food Consumption Statistics
- Healthline: The Effects of Fast Food on the Body
- Statista: Brand value of the 10 most valuable quick service restaurant brands worldwide in 2023
- Statista: Food and drink services
- Statista: Online Food Delivery – United States
- IBIS World: Fast Food Restaurants in the US – Market Size (2004–2029)
- Statista: Number of quick service restaurant (QSR) franchise establishments in the United States from 2007 to 2023, with a forecast for 2024
- BLS: Occupational Employment and Wage Statistics
- Plant-based Food: 2022 U.S. RETAIL SALES DATA FOR THE PLANT-BASED FOODS INDUSTRY
- Statista: Most common method used by consumers to get fast food during the coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19) in the United States as of November 2020
- Business Insider: Chipotle’s digital sales exploded 216% during the pandemic as most customers chose carryout despite many restaurants reopening their dining rooms
- IBIS World Fast Food Restaurants Industry Report







Write a comment
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required